Before we get into when pups lose their teeth, let’s have a look at puppy dentition. Puppies begin to develop teeth when they start the weaning process, usually around five to six weeks of age. However, it may take up to eight weeks for some breeds. The puppy dentition has 28 baby teeth, and pups are known to have sharp, pointy baby teeth that may wreak havoc on not just your shoes but also your hands, arms, and fingers. You have been warned. Let’s get started.
Do you have a specific question about puppies losing their baby teeth? Then use the table of contents below to jump to the most relevant section. And you can always go back by clicking on the black arrow in the right bottom corner of the page. Also, please note that some of the links in this article may be affiliate links. For more details, check the Disclosure section at the bottom of the page.
Here's what we'll cover:
Five Teething Stages For Dog
The First Teeth

When puppies begin weaning from milk, they begin to develop teeth. This usually begins at five or six weeks of age, while some dogs do not start until eight weeks old. There are 28’milk teeth,’ which are the canine equivalent of baby teeth. Puppy teething is excruciating.
They frequently begin nibbling at shoes and other items that are low to the ground and easy to find to release some of the strain in their mouths.
Puppies Lose Their Baby Teeth
Puppies lose their developing teeth faster than they emerge. Around one month after they appear, the baby teeth begin to fall out.
A puppy loses his first set of teeth at the age of three months. The incisors are usually the first to be removed. However, we shall go through this stage of puppy teething in greater detail below.
Four Month Molars
Around four months of age, a puppy’s adult molars begin to develop. At this point, nearly all of the baby teeth will have fallen out.
Puppies should see a veterinarian to find out how many other baby teeth they have.
Six Month Teeth Check

A puppy should have virtually all of its adult teeth in place by six months of age. Teeth growing crooked or producing an overbite in the dog may need to be repaired before the teething process is complete.
Correcting the teeth at this stage guarantees that no long-term harm occurs. Untreated teeth may make it difficult for the dog to eat in the future.
Adult dogs have 42 permanent teeth, which are normally all in by the time the puppy is eight months old.
The good news is that this is usually the point at which teething ceases. The bad news is that if you haven’t been working with your dog, he or she may continue to chew on objects for fun. You know how much harm a dog with 28 baby teeth can do to slippers. Consider the devastation 42 adult teeth will cause to your pricey work shoes!
It is critical to give acceptable chewing materials during the teething process. Use toys explicitly designed to aid in the teething process. To keep pups away from chewing furniture legs and shoes, use an anti-chew bitter spray.
While your puppy’s teeth are developing, it’s a great opportunity to prepare him or her for future success by teaching appropriate mouth manners, such as bite inhibition and the orders “Leave it!” and “Take it!”
When do puppies lose their baby teeth?
Puppies start teething at three weeks, and by six weeks, all of their deciduous teeth have erupted. The incisors (front teeth) and canine teeth (fangs) erupt first, followed by the premolars. There are no infant molars in dogs. The deciduous teeth begin to fall out at 12 weeks, and the permanent teeth begin to sprout. By six months of age, all permanent teeth should have erupted, and all deciduous teeth should have fallen out.
At What Age Do Puppies Get Their Permanent Teeth?

When the baby teeth begin to fall out, the permanent teeth start to sprout.
According to veterinarians, permanent teeth can appear as early as two months:
- incisors: 2-5 months
- Canine teeth at 5-6 months
- Premolars: 4-6 months
- Molars around 4-7 months (these only come in as part of the permanent set)
A dog should have all of his or her permanent teeth by the age of 7 or 8 months, for a total of 42 adult teeth.
Are there any common dental problems in young dogs?
Problems with deciduous teeth are uncommon. It is uncommon for a puppy to have a severe tooth condition to necessitate advanced intervention or referral to a veterinary dentist. Some breeds, especially smaller breeds, and brachycephalic (short-nosed) breeds, retain some of their deciduous teeth.
The upper canine teeth are the most commonly affected. However, it can occur elsewhere. Retained deciduous teeth can lead to malocclusion (misaligned teeth that result in a bad bite) and discomfort.
They also predispose dogs to tooth problems in the future. Food can become caught between the remaining deciduous teeth, permanent teeth, and gingiva (gums), resulting in periodontal (dental) disease. Retained deciduous teeth must be extracted.
It is usually a simple surgery that is done simultaneously with the pet’s neutering or spaying.
Caring For Your Puppy While Teething
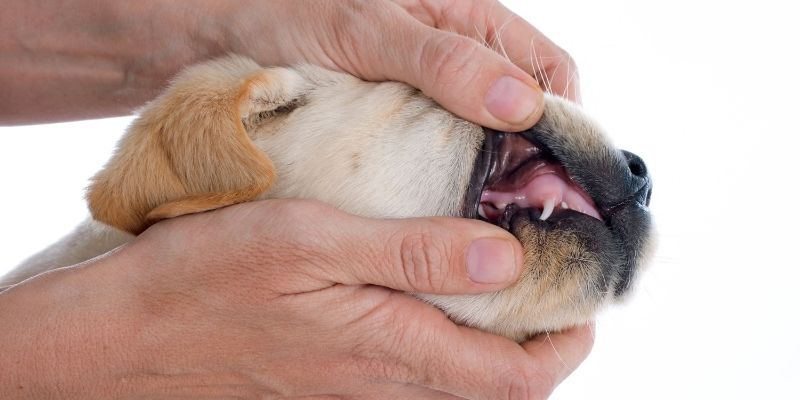
Teething should not be an issue if your puppy is healthy and happy, playful, eating, drinking, and socializing normally. However, if your puppy appears to be in pain or cannot eat or play, you should schedule an appointment with your veterinarian.
The greatest thing you can do for your teething puppy is to provide safe chew toys, which your veterinarian can prescribe.
Toys that are soft, flexible, and bend readily are ideal for teething puppies.
Toys that are difficult to bend and do not fit in your hand may be too rough on your puppy’s mouth and damage these sensitive young teeth.
What are good chewing toys for puppy teeth?
Because dogs chew on almost everything, almost everything has been discovered to create difficulties. This includes rawhides, pigs’ ears, and other animal parts given to dogs to chew (some owners swear by the “bully stick,” a dried or fried severed penis of a bull), bones, synthetic toys, tennis balls, and so on.
Some of these objects have caused gastrointestinal obstructions or intestinal punctures, which commonly necessitate surgery and can be fatal; others have caused dogs to asphyxiate by blocking the throat.

Regardless of these facts, remember that millions of dogs have been chewing millions of objects for years, with most of them going unnoticed. So, while the risk appears to be low, it cannot be eradicated, as with other hobbies. When your puppy starts chewing, keep an eye on him and consult with your veterinarian about the best chew toys for your dog. Even if your puppy is chewing on authorized toys, you should watch him because no toy is completely safe.
Keep in mind that even if an object is acceptable for ingestion or inhalation, it may not be beneficial for your dog’s teeth. Most veterinary dentists advise avoiding puppies and older dogs chewing on anything too hard. Objects made of nylon, as well as bones and antlers, would fall within this category. Veterinary dentists frequently summarize this advice by saying, “Don’t let your dog chew anything that won’t bend.”
Thanks for the blog graphics: Canva.com

Thanks for the blog graphics: Canva.com
Doghint.com is a participant of several affiliate programs. The list includes (but not limited to) the following: VigLink, Refersion, ShareASale, and Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a mean for us to earn fees by linking to Amazon.com and affiliated sites. Doghint.com does not intend to provide veterinary advice. All published articles are meant for informational purposes only and not substitute the professional veterinary consultation.


